EEG and tACS electrode montages and tACS current simulation results. A
4.8 (440) · $ 21.99 · In stock
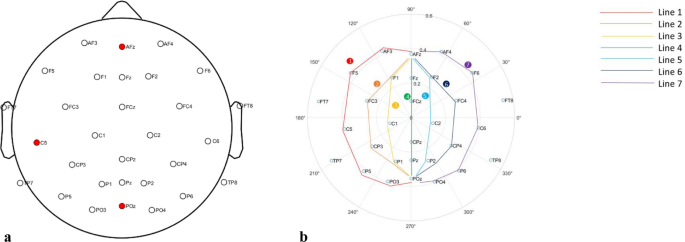
Download scientific diagram | EEG and tACS electrode montages and tACS current simulation results. A tACS ring electrode was centered position P3 of the international 10-20 system. EEG electrodes were positioned on P03, P04, Fz (ground) and both mastoids (references). tACS current simulations as created in SimNIBS show the norm of the electric field in V/m on an example brain, from three different viewpoints. from publication: “Broadband Alpha Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation”: Exploring a new biologically calibrated brain stimulation protocol | Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) can be used to study causal contributions of oscillatory brain mechanisms to cognition and behavior. For instance, individual alpha frequency (IAF) tACS was reported to enhance alpha power and impact visuospatial attention | Alpha, Transcranial direct current stimulation and Brain Stimulation | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
Behavioral Sciences, Free Full-Text

PDF) “Broadband Alpha Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation

Tom A. de Graaf's research works

Dose-dependent effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation on spike timing in awake nonhuman primates

The effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) at individual alpha peak frequency (iAPF) on motor cortex excitability in young and elderly adults
Frontiers Improving the Effect of Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS): A Systematic Review

Frequency-specific transcranial neuromodulation of oscillatory alpha power alters and predicts human visuospatial attention performance

Correlation between T1–T0 differences in the contrast estimates of
Phase-shifted tACS can modulate cortical alpha waves in human subjects
Directionality of the injected current targeting the P20/N20 source determines the efficacy of 140 Hz transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS)-induced aftereffects in the somatosensory cortex

Correlation between T1–T0 differences in the contrast estimates of

Phase-specific manipulation of rhythmic brain activity by transcranial alternating current stimulation - Brain Stimulation: Basic, Translational, and Clinical Research in Neuromodulation

Tom A. de Graaf's research works







