Socially-marketed rapid diagnostic tests and ACT in the private sector: ten years of experience in Cambodia, Malaria Journal
4.7 (736) · $ 17.00 · In stock
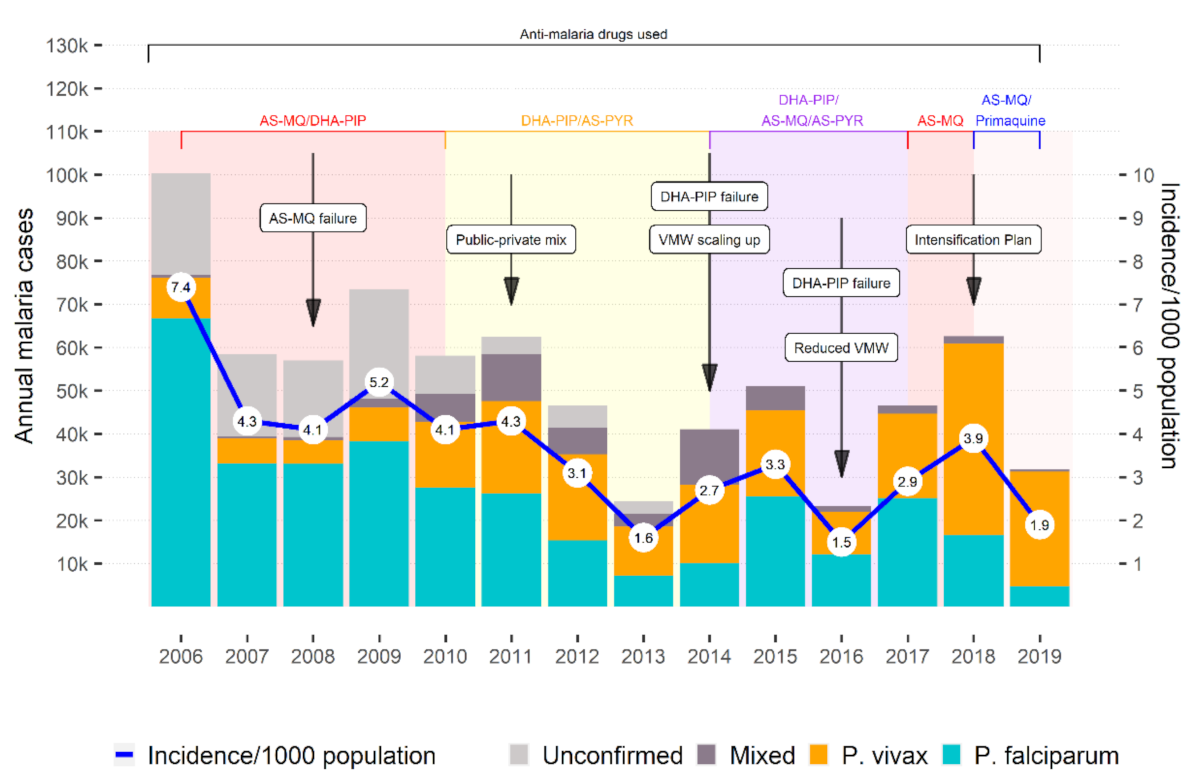
Whilst some populations have recently experienced dramatic declines in malaria, the majority of those most at risk of Plasmodium falciparum malaria still lack access to effective treatment with artemisinin combination therapy (ACT) and others are already facing parasites resistant to artemisinins. In this context, there is a crucial need to improve both access to and targeting of ACT through greater availability of good quality ACT and parasitological diagnosis. This is an issue of increasing urgency notably in the private commercial sector, which, in many countries, plays an important role in the provision of malaria treatment. The Affordable Medicines Facility for malaria (AMFm) is a recent initiative that aims to increase the provision of affordable ACT in public, private and NGO sectors through a manufacturer-level subsidy. However, to date, there is little documented experience in the programmatic implementation of subsidized ACT in the private sector. Cambodia is in the unique position of having more than 10 years of experience not only in implementing subsidized ACT, but also rapid diagnostic tests (RDT) as part of a nationwide social marketing programme. The programme includes behaviour change communication and the training of private providers as well as the sale and distribution of Malarine, the recommended ACT, and Malacheck, the RDT. This paper describes and evaluates this experience by drawing on the results of household and provider surveys conducted since the start of the programme. The available evidence suggests that providers' and consumers' awareness of Malarine increased rapidly, but that of Malacheck much less so. In addition, improvements in ACT and RDT availability and uptake were relatively slow, particularly in more remote areas. The lack of standardization in the survey methods and the gaps in the data highlight the importance of establishing a clear system for monitoring and evaluation for similar initiatives. Despite these limitations, a number of important lessons can still be learnt. These include the importance of a comprehensive communications strategy and of a sustained and reliable supply of products, with attention to the geographical reach of both. Other important challenges relate to the difficulty in incentivising providers and consumers not only to choose the recommended drug, but to precede this with a confirmatory blood test and ensure that providers adhere to the test results and patients to the treatment regime. In Cambodia, this is particularly complicated due to problems inherent to the drug itself and the emergence of artemisinin resistance.
IJERPH, Free Full-Text

Private Sector Contributions to National Malaria Surveillance Systems in Elimination Settings: Lessons Learned from Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, and Vietnam in: The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene Volume 108 Issue

Efficacy of three anti-malarial regimens for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Cambodia, 2009–2011: a randomized controlled trial and brief review, Malaria Journal

Private sector role, readiness and performance for malaria case management in Uganda, 2015, Malaria Journal

Expert perspectives on the introduction of Triple Artemisinin-based Combination Therapies (TACTs) in Southeast Asia: a Delphi study, BMC Public Health

PDF) Testing times: trends in availability, price, and market share of malaria diagnostics in the public and private healthcare sector across eight sub-Saharan African countries from 2009 to 2015

Tackling Substandard and Falsified Medicines in the Mekong: National Responses and Regional Prospects - Lamy - 2015 - Asia & the Pacific Policy Studies - Wiley Online Library

Private Sector Contributions to National Malaria Surveillance Systems in Elimination Settings: Lessons Learned from Cambodia, Lao PDR, Myanmar, and Vietnam in: The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene Volume 108 Issue

Quality of Antimalarials at the Epicenter of Antimalarial Drug Resistance: Results from an Overt and Mystery Client Survey in Cambodia in: The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene Volume 92 Issue







